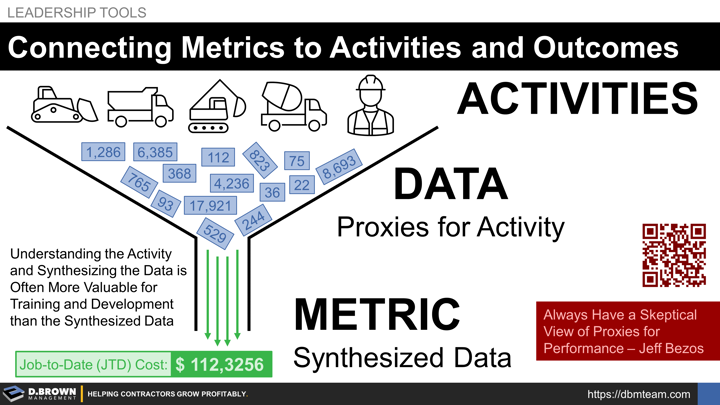
Remember that deeply understanding the activity by either doing it, or through rigorous work observation is where it all starts. Understanding how the activity is connected to outcomes is the foundation.
When it comes to training and development, studying the activity, collecting the data, and synthesizing that data into metrics, especially trends over time and ratios that put it into context is far more valuable than just being presented the synthesized data.
Remember that we are all in the process of working our way up the Knowledge Management Pyramid in some way. Skipping steps leaves major holes in our Situational Awareness and therefore puts decision making at risk. This is one of the areas where Scoreboards and Scorecards fail to deliver results.
The metrics used on scoreboards and scorecards were often first developed by someone at a higher level who:
- Understood the connection between the activities and the outcomes expected.
- Understood how to collect the data that represented the activities.
- Understood how that data was synthesized into the metric.
- Knew what that metric should be as compared to what and when.
- Could quickly unpack that synthesized metric into its component data and activities.
- Understood what actions to take (or not) based on that metric and deeper investigation.
- Build this metric into a clear accountability in a job role description – “Bring in projects at or under budget.”
- Built this metric into a great automated information system that displays that metric quickly to everyone who needs to know it.
To someone new who is learning and developing up the organization, they won’t have all this background and experience.
- They will understand the accountability.
- They will see the metric.
- They won’t make consistently good decisions that improve outcomes.
Something as simple as JTD cost doesn’t even include all the same things depending on the contractor. JTD cost is only relevant if we know:
- Total budget and
- Current JTD percentage complete so we can
- Compare our JTD cost to where we should be and
- What action to take if required including deeper investigation.
Jeff Bezos who built an exceptionally data-driven company describes how important having a skeptical view of these proxies for performance is (short video clip)
Charles Duhigg gives great examples of this in Chapter 8 (Absorbing Data) from Better, Faster, Smarter